mba meaning takes center stage as we dive into the significance of this advanced degree in today’s business landscape. An MBA, or Master of Business Administration, is not just a title; it’s a powerful credential that opens doors to various career opportunities and can greatly influence earning potential. With a plethora of specializations ranging from finance to marketing, an MBA equips graduates with the skills necessary to navigate the complexities of modern business.
The typical structure of an MBA program includes core subjects alongside elective courses, providing a comprehensive education that caters to individual interests. Whether you choose to pursue your MBA full-time, part-time, or online, there are options available to fit diverse lifestyles and commitments. Understanding the format of different programs can further assist prospective students in making an informed decision about their educational journey.
Definition and Importance of MBA

An MBA, or Master of Business Administration, is a graduate degree that equips individuals with the skills needed to excel in various business environments. This program typically covers a wide range of business-related topics such as finance, marketing, operations, and management. The significance of an MBA in the business world cannot be overstated; it not only enhances an individual’s knowledge but also provides a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business landscape.
The importance of an MBA lies in its ability to prepare graduates for leadership roles and strategic decision-making positions within organizations. The curriculum is designed to foster critical thinking, analytical skills, and effective communication, all of which are essential for success in the business arena. Furthermore, an MBA can significantly impact career advancement and earning potential. According to various studies, MBA graduates often experience higher starting salaries and greater career progression compared to their counterparts without advanced degrees.
Specializations within MBA Programs
MBA programs offer a range of specializations, allowing students to tailor their education to their career goals and interests. Some of the most popular specializations include:
- Marketing: Focuses on strategies for promoting and selling products or services, understanding consumer behavior, and managing brand value.
- Finance: Covers investment analysis, financial management, and corporate finance, preparing students for roles in investment banking, financial planning, and accounting.
- Operations Management: Emphasizes the efficient production and delivery of goods and services, encompassing supply chain management and process optimization.
- Human Resources: Involves managing employee relations, organizational culture, and talent acquisition strategies.
- Entrepreneurship: Encourages innovation and startup development, teaching students how to launch and grow new ventures.
Each specialization provides unique insights and skills that can be directly applied in various sectors of the economy, enabling graduates to become experts in their chosen fields.
Impact on Career Advancement and Earning Potential, Mba meaning
An MBA significantly enhances career advancement opportunities and earning potential for graduates. Employers often seek candidates with advanced degrees for leadership and management positions, which can lead to greater responsibilities and higher salaries. The following statistics highlight the financial benefits of obtaining an MBA:
- Increased Salaries: MBA graduates can earn, on average, 50% more than their peers with only a bachelor’s degree. For instance, graduates from top programs may start with salaries exceeding $100,000.
- Job Opportunities: Many companies prioritize MBA graduates for management positions, making them more competitive in the job market.
- Career Flexibility: An MBA opens doors to a variety of industries, allowing graduates to transition into fields such as consulting, finance, healthcare, or technology.
The value of an MBA extends beyond just financial gain; it fosters a network of professionals, providing access to mentoring, collaboration, and career opportunities that can propel one’s career forward.
MBA Program Structure
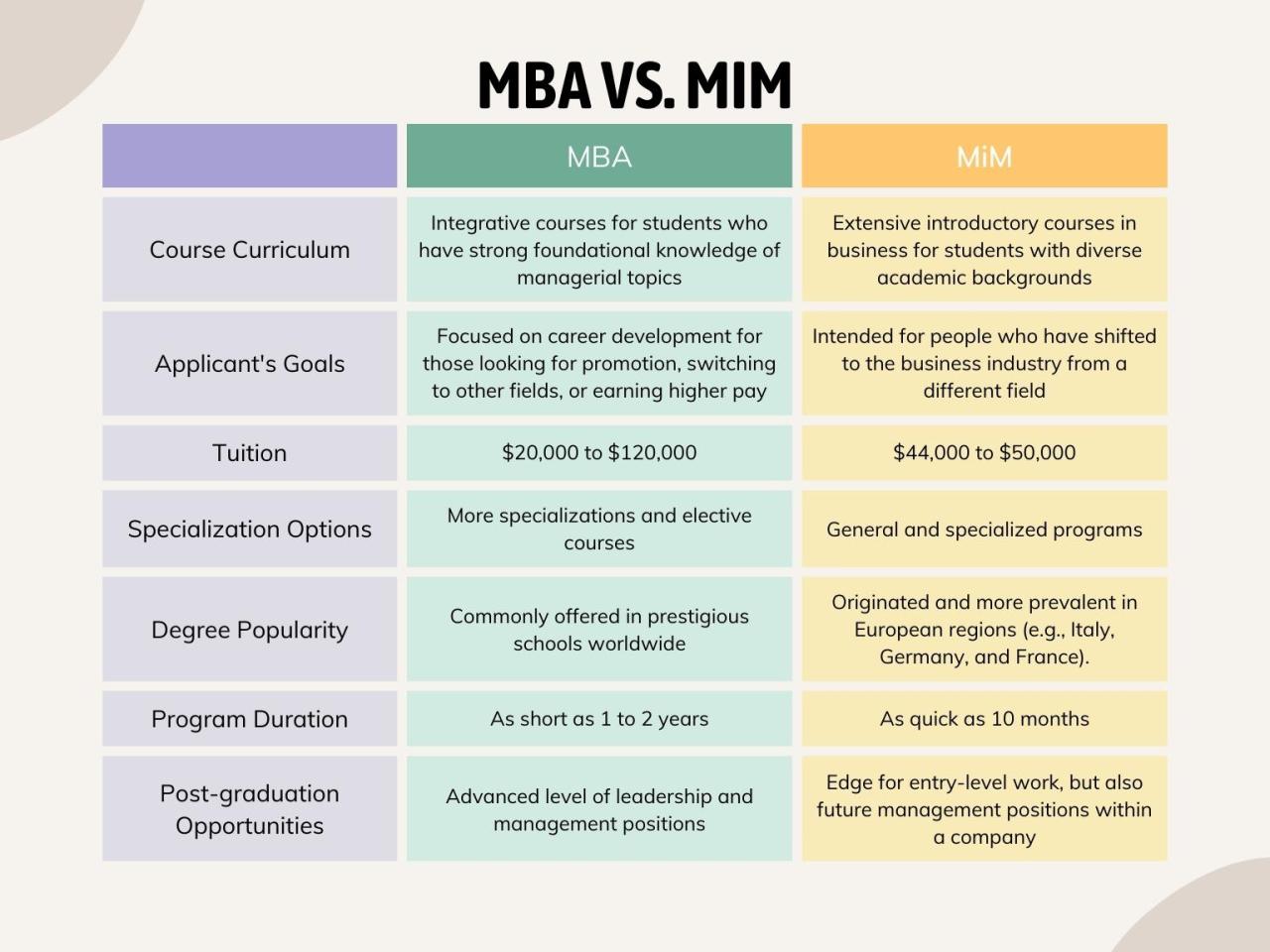
An MBA program is designed to equip students with a comprehensive understanding of business management principles. The structure of these programs typically includes a blend of core and elective courses that prepare graduates for various roles in the business world. This combination allows students to gain essential knowledge while also providing the flexibility to tailor their education to meet specific career aspirations.
The typical MBA program is structured around a series of core courses that cover fundamental business topics such as finance, marketing, operations, and strategy. These are complemented by elective courses, enabling students to focus on areas of interest or specialization. The flexibility of MBA programs also extends to their delivery methods, accommodating the diverse needs of students.
Core and Elective Courses
Core courses form the backbone of the MBA curriculum, ensuring that all students acquire the fundamental skills necessary for effective management. The following are common core subjects:
- Financial Accounting
- Managerial Economics
- Organizational Behavior
- Marketing Management
- Operations Management
- Corporate Finance
- Strategic Management
Elective courses allow students to delve deeper into specific interests or industries. These may include:
- Entrepreneurship
- Data Analytics
- Supply Chain Management
- International Business
- Human Resource Management
Delivery Methods for MBA Programs
MBA programs cater to a variety of student needs by offering different methods of delivery. The most common formats include full-time, part-time, and online options, each with unique advantages.
Full-time programs typically require students to dedicate their entire schedule to their studies, often enabling them to complete the degree in two years. Part-time programs offer flexibility for working professionals, allowing them to balance work and studies over a longer period, often three years or more. Online programs provide the ultimate flexibility, allowing students to complete coursework at their own pace, making education accessible regardless of location.
Comparison Table of MBA Program Formats
The following table highlights different MBA program formats offered by popular universities, showcasing their unique characteristics.
| University | Program Format | Duration | Specializations Available |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard Business School | Full-time | 2 years | Finance, Marketing, Entrepreneurship |
| Wharton School, UPenn | Part-time | 3-4 years | Healthcare, Real Estate, Operations |
| Northwestern University (Kellogg) | Online | 1-2 years | Digital Marketing, Strategy |
| Columbia Business School | Full-time | 2 years | Finance, Management, Marketing |
| University of Michigan (Ross) | Part-time | 3-5 years | Operations, Information Systems |
“The structure of an MBA program is crucial in shaping the future leaders of industry.”
Skills Acquired Through an MBA: Mba Meaning
An MBA program is designed to equip students with a diverse set of skills needed to thrive in the complex world of business. These skills range from analytical thinking to leadership capabilities, enabling graduates to navigate various challenges faced in the workplace. As they progress through their studies, MBA students not only absorb theoretical knowledge but also engage in practical applications that prepare them for real-world scenarios.
The curriculum of an MBA program is structured to foster both hard and soft skills. Hard skills are typically quantitative, focusing on specific technical expertise, while soft skills are more interpersonal and emotional in nature. Together, these skill sets play a crucial role in any industry, significantly enhancing a graduate’s employability and effectiveness in the business environment.
Key Skills Developed in an MBA
The following list identifies important skills obtained through an MBA program and provides insight into their application in various industries:
- Leadership: Students learn to inspire and guide teams towards achieving organizational goals, a vital skill in management roles across all industries.
- Analytical Thinking: Developing the ability to assess complex business problems through data analysis allows graduates to make informed decisions that influence strategies and outcomes.
- Financial Acumen: Understanding financial statements and investment strategies equips graduates to manage budgets and financial planning effectively in businesses.
- Marketing Expertise: An MBA helps students grasp market analysis and consumer behavior, which is critical for roles in marketing and sales sectors.
- Communication Skills: The program emphasizes both verbal and written communication, essential for networking, pitching ideas, and collaborating with colleagues and clients.
- Project Management: Students learn to plan, execute, and oversee projects, ensuring they meet deadlines and stay within budget, a necessary skill in various fields.
- Negotiation Skills: Developing negotiation techniques aids graduates in reaching agreements that benefit their organization, particularly in sales and procurement.
Application of Skills in Real-World Scenarios
The skills acquired through an MBA are applied in numerous ways in the business world. For instance, a graduate working within a tech startup might leverage their leadership training to rally a team around a new project, ensuring that everyone understands their role and feels motivated.
In finance, an MBA graduate might use their analytical thinking to assess market trends and make investment recommendations, ultimately driving the company’s profitability. Marketing professionals apply their understanding of consumer behavior to launch campaigns that resonate with target audiences, enhancing brand visibility and customer loyalty.
Moreover, strong communication skills gained from an MBA enable graduates to present ideas confidently in board meetings or to negotiate contracts with suppliers effectively. These soft skills are just as critical in shaping a professional’s success as the hard skills they acquire.
“The integration of hard and soft skills in an MBA curriculum creates well-rounded leaders capable of adapting to diverse challenges in the workforce.”
In summary, the variety of skills acquired through an MBA program prepares graduates for multiple business environments, ensuring they are ready to tackle real-world challenges head-on and drive organizational success.
Career Opportunities Post-MBA

An MBA degree can open a wide array of career opportunities across various industries. Graduates often find themselves in leadership roles, contributing to organizational growth and innovation. The versatility of an MBA allows professionals to pivot into different sectors, enhancing their marketability and earning potential.
The journey after obtaining an MBA can lead to numerous pathways, including finance, consulting, marketing, and entrepreneurship. Each of these sectors offers unique roles that leverage the skills acquired during the MBA program. Networking, strategic decision-making, and analytical thinking are just a few of the competencies that help MBA graduates excel in their chosen careers.
Various Career Paths for MBA Graduates
Many MBA graduates find success in diverse roles across industries. Below is a list of some of the most popular career paths:
- Management Consultant: Focuses on improving organizational efficiency.
- Investment Banker: Involves raising capital, advising on mergers and acquisitions.
- Marketing Manager: Responsible for developing product strategies and leading marketing campaigns.
- Operations Manager: Oversees production processes and supply chain logistics.
- Entrepreneur: Starts and manages their own business ventures.
The availability of these roles often depends on industry demand and individual skill sets. MBA graduates are typically equipped with the tools necessary to adapt and thrive in various positions.
Notable MBA Alumni Success Stories
Many successful figures in business and leadership have earned their MBAs. These alumni serve as inspirations, showcasing the potential of MBA graduates. Some notable examples include:
Howard Schultz, former CEO of Starbucks, revolutionized the coffee industry using principles learned during his MBA.
Sheryl Sandberg, COO of Facebook, has led the company to remarkable growth, applying strategic insights from her MBA experience.
These individuals exemplify how an MBA can be a catalyst for transformative leadership and innovation.
Industry and Role Categorization
To better understand the career landscape post-MBA, here is a table categorizing various industries and suitable roles for MBA holders:
| Industry | Roles |
|---|---|
| Finance | Financial Analyst, Investment Banker, Risk Manager |
| Consulting | Management Consultant, Business Analyst |
| Marketing | Brand Manager, Marketing Director, Digital Marketing Specialist |
| Technology | Product Manager, IT Consultant, Data Analyst |
| Healthcare | Healthcare Administrator, Consultant, Operations Manager |
| Entrepreneurship | Startup Founder, Business Development Manager |
This table helps illustrate the breadth of options available to MBA graduates, showcasing how their skills can be applied in various settings. Each industry offers unique challenges and opportunities, allowing graduates to find their niche in the business world.